heat recovery - renewable and energy efficient heating and cooling - distributed power generation
Overview
EINSTEIN is a Tool & Methodology for the design of energy efficient (thermal) energy supply systems, both as retrofit in existing systems and for green field design.
The major modules of EINSTEIN are providing support for:
- Data collection and screening (consistency and completeness checking)
- Assisted design of appropriate heating and cooling supply and heat recovery systems: conceptual design and pre-dimensioning.
- Energy, economic and environmental evaluation, including comparative analysis of different options
- Structured reporting
Methodology
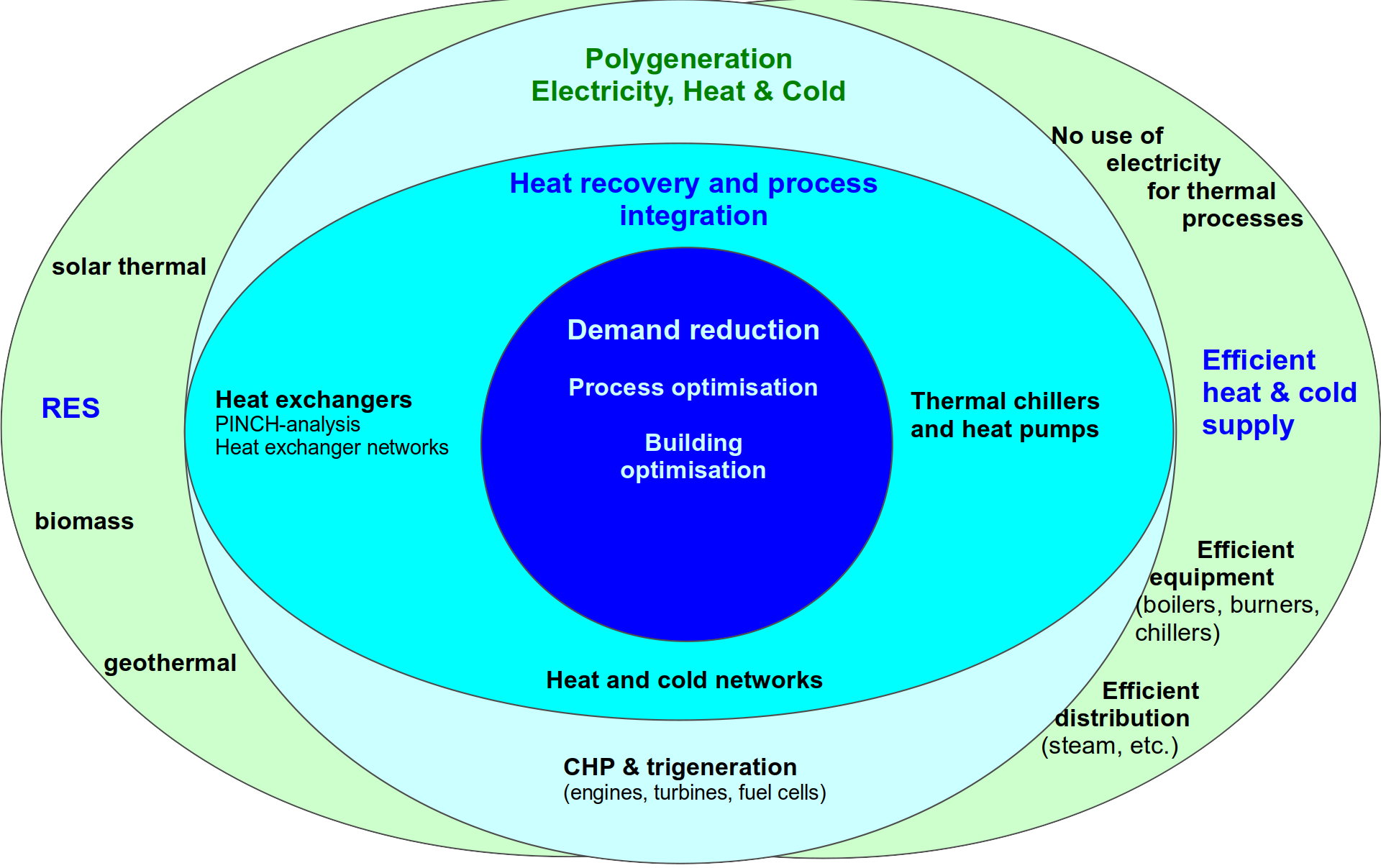
EINSTEIN is based on a structured approach to optimisation of energy supply.
The major components of the EINSTEIN methodology are:
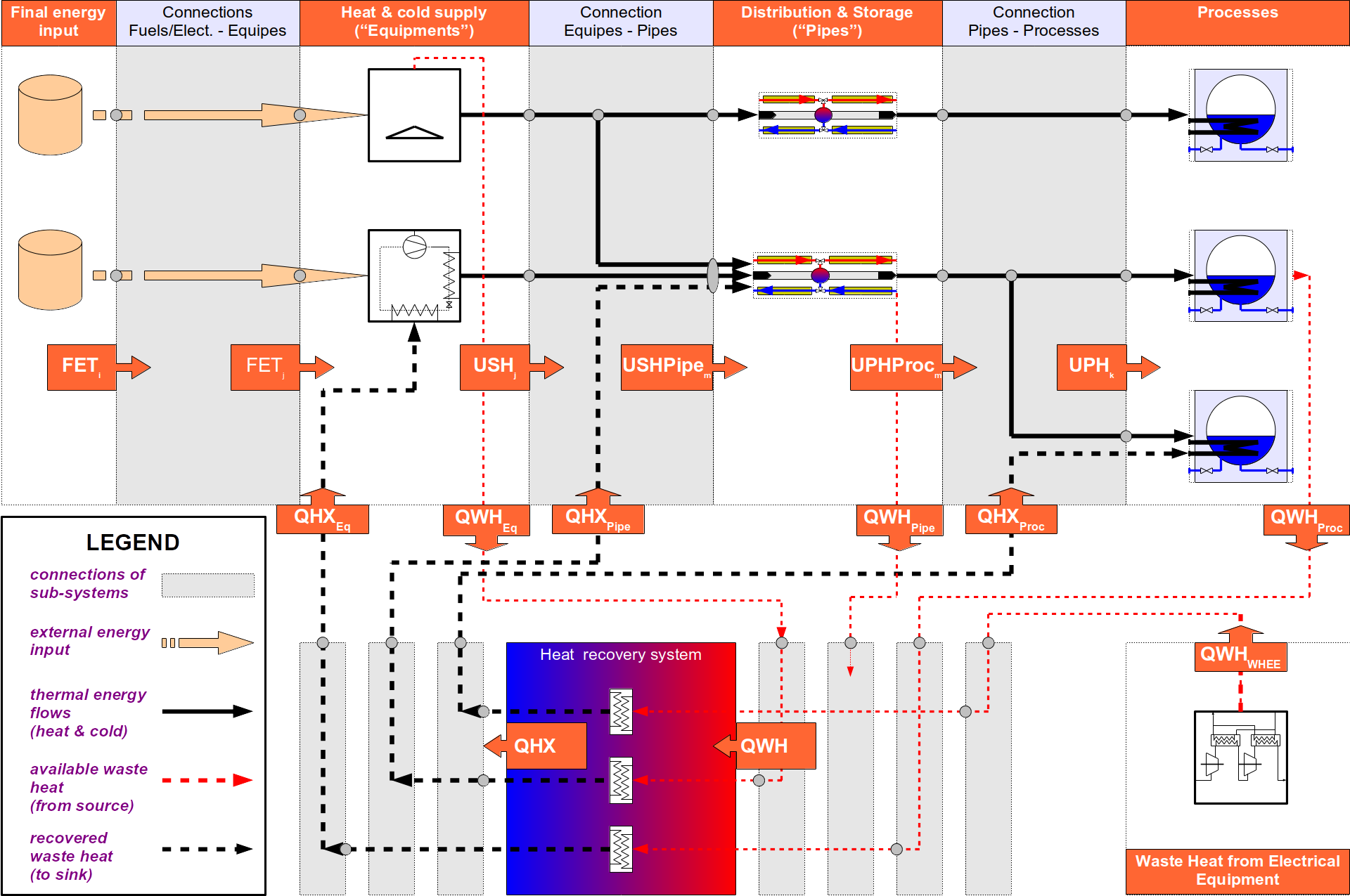
- a standard for the accountancy of energy flows in a plant, including a system of definitions of quantities, subsystem boundaries and temperature levels. The latter are very important for exergy optimisation (e.g. heat pump application or heat exchanger networks).
- standards for economic and environmental analysis. the outcome of this type of analysis depends strongly on basic apriori assumptions and optimisation targets. The EINSTEIN methodology pretends to provide transparency and awareness about these parameters and their impact on the assessment results.
Software
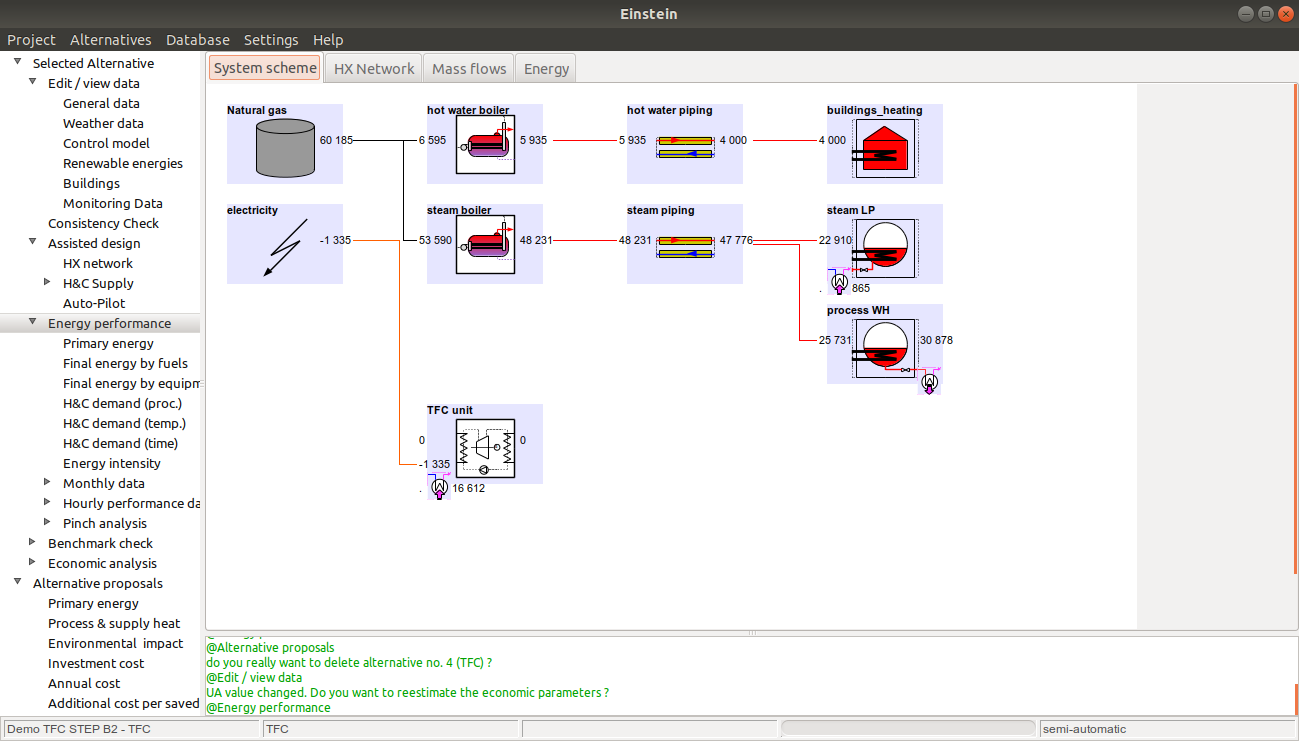
The EINSTEIN software guides the user through the whole design process spanning from data acquisition, processing and estimation to the design and quantitative (energy and economic) evaluation of alternative design options.
The EINSTEIN software contains as major features:
- structured data collection and processing (status-quo; definition/forecasting of requirements), including consistency and completeness checking and data estimation where necessary
- data analysis giving a detailed breakdown of energy consumption as a function of time and temperature level
- assisted design of system options (incl. pinch analysis, algortithms for selection of appropriate technologies and predimensioning of new equipment)#
- dynamic system simulation, supporting „quick set-up“ of simulations without need for large amount of input settigns (e.g. no need for manual configuration of system hydraulics or control strategies)
- economic and environmental analysis
- structured semi-automatic reporting
